The Leading European Countries in Coffee Production and Imports in 2024
In 2024, European Union (EU) countries continue to solidify their role in the global coffee industry, with both production and imports showing significant activity. According to the latest Eurostat data, coffee production in the EU has increased by 15% over the past decade, reflecting the growing demand and cultural significance of coffee across the continent.
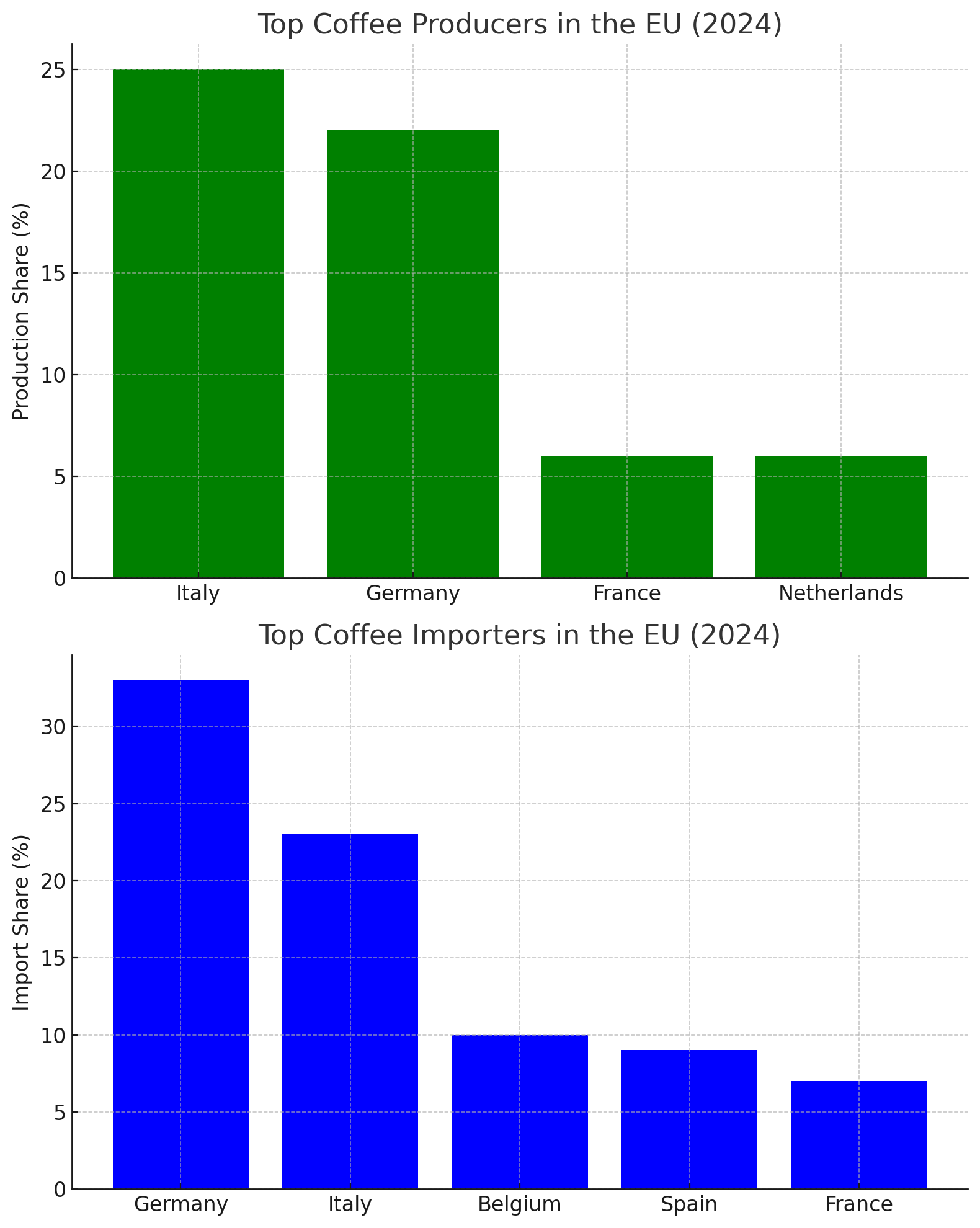
Top Coffee Producers in the EU
Italy stands as the top coffee producer within the EU, contributing 25% of the total production. Following Italy is Germany, which accounts for 22%, while France and the Netherlands each contribute 6%. Together, these countries lead Europe’s coffee production, which surpassed 2 million tonnes in 2023, including roasted, decaffeinated, and substitute coffee products. This output is valued at approximately €13 billion.
Major Coffee Importers in the EU
In addition to robust production, the EU also plays a dominant role in coffee imports, with nearly 2.7 million tonnes entering the bloc annually, valued at €10.6 billion. Germany leads in coffee imports, purchasing 33% of the EU’s total coffee supply. Italy follows with 23%, while Belgium (10%), Spain (9%), and France (7%) also represent key importers.
Brazil remains the EU’s largest coffee supplier, responsible for 34% of the total coffee imports into the EU, equating to around 921,900 tonnes in 2023. Vietnam and Uganda follow, supplying 24% and 8% of the imports, respectively.
New Challenges on the Horizon: Sustainability Regulations
The EU’s coffee industry, however, faces significant changes with a new law set to take effect in 2025. This legislation will require coffee companies to ensure their supply chains do not contribute to deforestation. This move follows reports indicating that the EU, as the world’s largest coffee importer, is responsible for 44% of coffee-related deforestation globally.
The French government’s data confirms that coffee is a crop with a high deforestation potential, and the new law is seen as a crucial step towards addressing the environmental impact of coffee production and consumption. Coffee-producing countries and companies will need to adapt to these new regulations, which could potentially reshape the landscape of the industry.
Global Coffee Trends and Market Overview
Globally, Brazil continues to dominate coffee production, producing an average of 3 million tonnes annually. Vietnam and Colombia follow as the next largest producers. Despite the massive scale of the industry, it is primarily driven by small family farms, which make up 70% of global coffee production.
With over 2 billion coffee consumers worldwide and 25 million people working in the industry, coffee remains one of the world’s most valuable agricultural commodities. However, the share of value reaching coffee-producing countries has diminished over the past two decades, with profits increasingly captured by large industry players in consumer markets.
Sustainability in the Coffee Sector
The issue of sustainability has become central to the future of coffee production and trade. About 55% of the world’s coffee production is now covered by certifications such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance, and organic standards, which aim to promote fairer and more sustainable coffee supply chains.
In Europe, organizations such as the European Coffee Federation and global initiatives like the Sustainable Coffee Challenge are working to ensure that the coffee industry becomes more transparent and sustainable, addressing both environmental and social issues specific to coffee-growing regions.
Conclusion: The Future of Coffee in Europe
As we move through 2024, European countries remain at the forefront of global coffee production and imports. However, the introduction of new sustainability regulations in the coming years may reshape how coffee is sourced and sold in the EU. The balance between maintaining the EU’s leading position in the coffee market and addressing environmental concerns will be critical for the industry’s future.
Europe’s love for coffee remains as strong as ever, but how the industry adapts to these changes will define its path in the years to come.



